Clubfoot: diagnosis and treatment
The clubfoot is the foot’s genetic deformity where the foot is turned inward or downward. It is one of the most common congenital pathologies, since one infant in every 1.000 live births will have clubfoot.
The clubfoot diagnosis is really simple; you can see it with the naked eye. Even doctors can detect it during the ultrasound examinations before giving birth.
Clubfoot is not painful and nowadays proper treatments give to the majority of children a wide range of physical activities. This deformity can be corrected when the patient is an infant through the manual manipulation of foot. The surgical treatment can be followed in more complicated cases.
Clubfoot’s causes
Researchers are still uncertain about the clubfoot’s cause. The most widely accepted theory is that this disease is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors:
- The clubfoot’s history in the family.
- Another congenit diseases like the spina bifida.
- The environment during the pregnancy: tobacco, drugs, and so on.
- Shortage/little (of ) amniotic liquid during the pregnancy.
Symptoms of clubfoot
Clubfoot is not painful; however, we can appreciate physical symptoms. The principal symptoms are:
- The superior part of the foot is turned inward and downward, with toes pointing toward the opposite foot. This deformity makes the foot curve more accentuated.
- Muscles and tendons are underdeveloped on the affected side.
- The affected foot can be smaller than the other, until 1 centimetre.
Treatment
Nowadays, this deformity is treated after birth with manipulation or surgery. It is recommendable to start these treatments some weeks after the birth, since the infant’s bones and tendons are more flexible.
It is possible to completely correct the clubfoot deformity with this method, so the children will not have any symptoms while walking.
If the manipulation treatment does not work or the disease is complicated, we can always resort to the corrective surgery. The surgeon will extend the tendons to replace the foot in the correct position. After the operation, the child must wear a plaster and subsequently an immobilization device.
However, doctors can find older people with complications when walking. These older people’s complications occur because they were not diagnosed before.
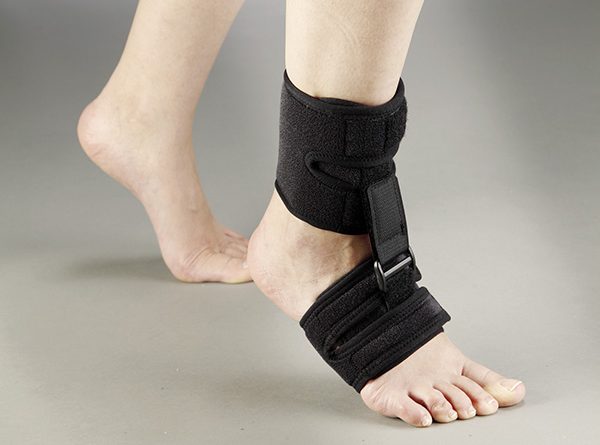
The person frequently walks on the metatarsal region in these cases, in other words; tiptoeing. We have Artroben splints for the tiptoeing problem. This splint obtains a better walking condition, since it permits the plantar flexion in the heel support.
Moreover, there is also the possibility to have clubfoot in adults that had had a neurological injury as an ictus. In that case, the patient can use the splint mentioned before, as well as various exercises and stretching to try to return some mobility to the area.
Find our products in your Pharmacy or Orthopedics. Consult here your nearest point of sale.